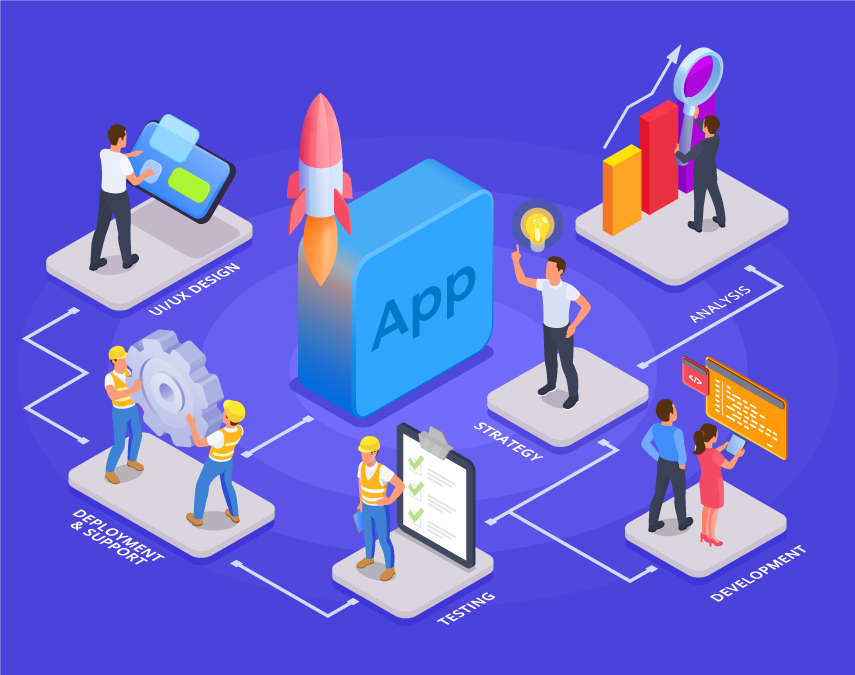

Top 5 Mobile App Development Trends to Watch in 2026
The mobile application market is in a state of unprecedented development that has been propelled by high-technological change and increased demands of users. By 2026, mobile applications cease to be mere tools, but they are smart platforms that drive digital experiences, business processes, and customer experiences. The trends that define the future of mobile app development should be grasped by the companies that intend to remain competitive and change their strategies in line with them. The article examines the five most popular trends in mobile app development that are destined to affect the way apps are developed, deployed, and experienced in 2026 and the reasons why they will be important to both businesses and developers.
AI-Powered Mobile Apps Become the New Standard:
AI is never bedded in as a value added feature in mobile app anymore it is developing into a standard feature. Integration of AI in 2026 will be at the center of provision of smarter, personalized and more efficient user experiences. Mobile applications are gaining more and more possibilities in recognizing user behavior, anticipating their preferences, and real-time content customization. Personalization through AI enables apps to offer suggestions, alerts and user interfaces depending on personal usage. As examples, e-commerce apps can be more accurate in suggesting goods, whereas fitness and health apps can offer more tailored advice based on the data provided by the user. In addition to personalization, AI can improve voice recognition, image processing, chatbots, and predictive analytics, making the apps more interactive and intuitive. In terms of development, AI is also the best to streamline the backend operations through automation of data analysis, enhanced performance monitoring, and anomaly detection prior to impacting users. With the increased availability of AI frameworks, even small and midsized businesses would be able to create smart mobile apps that can compete with those at the enterprise level.
Cross-Platform Development Gains Greater Maturity:
In 2026, cross-platform frameworks become even more popular, and at the same time, they become more mature and reliable. Flutter, React Native, and Kotlin Multiplatform are the technologies that allow developers to create high-performance apps with a single codebase that has almost-native user experiences. The main strength of a cross-platform development is efficiency. Companies are able to significantly cut down the development time and expenses and at the same time reach users on both iOS and Android. These frameworks provide better rendering engines, better hardware integration, and better support of platform-specific features in 2026. To the users, the advantage is consistency. The apps are similar to the behavior and experience of different devices, which brings a cohesive brand positioning. To businesses, a faster release cycle implies a faster entry into the market and more frequent release. This will be the method of choice when starting off or in an existing business as frameworks continue to bridge the divide between native and cross-platform performances.
Enhanced Mobile App Security Takes Center Stage:
As digital services increase the security risk increases. Mobile app security will be prioritized in 2026 as cyber-attacks will be more complex, and data privacy laws will become more stringent. The users are more conscious of the way their information is processed, and any violation may have disastrous reputational and financial consequences. New mobile applications are adopting superior security controls including biometric authentication, end-to-end encryption, secure API and AI-based threat detection. Real time identification of suspicious activity is also being accomplished through behavioral analytics so that apps can take precautionary action against potential attacks. Considering the aspect of development, security is becoming left shifted in the development lifecycle. Not only are secure coding, automated vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks now part of CI/CD pipelines but are also linked to them. Security is no longer an issue that is implemented after deployment but rather a design consideration. Firms that are keen on the security of their mobile applications will gain the confidence of their users and gain sustainability in the long run.
5G and Edge Computing Unlock New Performance Levels:
The 5G networks that have been adopted widely are changing the capabilities of mobile applications. The data speeds will be faster, latency will be lower and network reliability will be enhanced in 2026, enabling developers to create more rich and responsive applications. This is especially effective on apps that need real-time interactions like gaming, streaming, augmented reality and IoT-based services. Edge computing also increases performance by enabling data processing near the user instead of it being centralized on cloud servers alone. This saves time wastage and enhances responsiveness particularly on applications that need real time response. As an example, a route can be updated immediately with the help of navigation applications, and smart health applications can process data in real time. In the case of business, such a combination provides chances to provide advanced features otherwise impossible on mobile devices. The developers are now required to develop apps exploiting 5G possibilities and remain efficient to users in areas with lower connectivity.
Immersive Experiences Through AR and Advanced UI/UX:
The expectations of users to mobile apps have never been high. Immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR) will cease to be a novelty and become a tool to use in industries in 2026. Retail applications make use of AR to enable customers to see products in their surroundings whereas education and training applications develop interactions in learning. Meanwhile, UI/UX design is undergoing changes as a means to accommodate such immersive interactions. Gesture interface, motion feedback, and intelligent layouts are on the rise. Apps are created in a way that is more natural and intuitive and less consumes cognitive load and more engages users. Accessibility is also a key factor in the current trends in UI/UX. When apps are designed inclusively, it means that individuals with a variety of abilities can use them, meaning that accessibility is not only a compliance measure but a competitive edge. The future of mobile apps will be seen in the visual, emotionally responsive and universally accessible experiences.
Why These Trends Matter for Businesses:
These trends of mobile app development are not only technical innovations, but they have a straight face to business success. With AI-driven personalization, there is increased engagement and retention. Cross-platform development saves time-to-market and cost. Safety on a higher-level safeguards brand identity and consumer confidence. 5G and edge computing make it possible to offer innovative services, and immersive design makes users more loyal. Firms, which match their mobile strategy with these trends, are in a position to respond to such demands in the future and outcome with other firms. Instead, they should be ignored at the risk of being left behind in a market where the expectations of users keep changing at a very fast pace.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Mobile Future in 2026
The intelligence, speed, security, and immersive user experiences are the characteristics of the mobile app landscape in 2026. New technologies are transforming the methods of creation of apps and interaction between them and users. On the side of the developers, this entails adoption of new tools and frameworks. In the case of businesses, it translates into investing in mobile solutions that are future-ready, scalable as the business grows and becomes innovative.
These five best trends in the mobile application development are the ones that by comprehending and embracing them, organizations are able to create applications that are not only effective, but progressive. The apps that will be successful in 2026 are those that will be made with flexibility, user confidence and technological perfection.

The Next Generation of Quality Assurance Automated Testing in 2026
The last decade has seen a drastic change in software quality assurance and automated testing is at the heart of this revolution in 2026. With the increasing complexity of software systems and the decreasing release cycles, manual testing has ceased to be enough to guarantee speed, accuracy and reliability. Companies are now demanding quicker deployments and quality has not been violated, automated testing has taken the position of being the foundation of the current QA plans. The following generation of quality assurance is not merely about locating bugs but eliminating them, anticipating them and further developing software performance during the lifecycle of its development. In the year 2026, every phase of software development will be highly integrated with automated testing. Since the creation of the code to its deployment and post-release monitoring, the testing ceases to be a different phase but a continuous, smart process. The change enables teams to develop high quality applications at scale without compromising consistency across platforms, devices and user environments.
From Manual to Intelligent Automation:
The scope of the work of QA teams has been greatly extended. Although manual testing is still used in exploration and usability testing, most repetitive, regression and performance testing is now automated. The automated testing frameworks can today deal with complex situations that would have previously taken considerable number of human resources. These tools are used to imitate actual user interaction in many different environments thus guaranteeing consistent behavior in the diverse conditions. By 2026, scripted test cases become a thing of the past. The intelligent testing systems are able to understand changes in an application and produce appropriate test cases automatically. This minimizes maintenance overhead and makes testing develop with the codebase. The QA professionals have become strategists and analysts, which involves designing tests, risk assessment, and optimizing quality, as opposed to running repetitive tasks.
AI-Driven Test Case Generation and Maintenance:
Automated testing has become a household name with the introduction of artificial intelligence. Intelligent testing applications can understand the requirements of an application, user stories and even source code to create extensive test scenarios. This helps enormously to cover more test cases and reduces the chances of omissions of critical edge cases. Test maintenance, which is traditionally one of the most time-consuming elements of automation, is also changed. AI-driven systems automatically update test scripts whenever the UI elements change, or the workflow is modified rather than fail. These tools constantly optimize the accuracy of tests by examining test history and errors in order to determine how the tests can be optimized. Consequently, this generates time savings in testing by QA teams, who can now focus on bettering the company product in general.
Shift-Left Testing Becomes the Standard:
This notion of shift-left testing that brings testing to the development process at earlier stages has become a self-governing norm by 2026. There is now direct integration of automated testing tools with development environments, enabling developers to run tests as they code. Such early identification of flaws avert problems spread to the late part of the lifecycle where corrections prove to be even costly and time consuming. The automatically triggered unit tests, integration tests, and security scans are done when code is committed. It is a culture of quality ownership among the team because developers can fix mistakes during their initial development cycles, as they receive constant feedback loops that make them feel at ease making mistakes and fixing them. It is a proactive strategy that minimizes defects in products and enhances the cooperation between engineers in charge of quality assurance and those developing products.
Continuous Testing in CI/CD Pipelines:
Modern software delivery is based on continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and automated testing is one of the essential elements of the pipeline in 2026. Each change of code generates a series of automated tests that prove functionality, performance and security. It is only the builds which pass through the quality threshold which have been predefined that proceed in the pipeline. Advanced test orchestration systems are smart enough to focus on the order of executing the tests depending on riskiness, changes made, and past failure history. This is a guarantee of quicker feedback without coverage loss. With the introduction of automated testing into the CI/CD workflows, organizations can experience faster release, greater confidence, and less downtime.
Cross-Platform and Device Testing at Scale:
Applications and devices operate on a wide range of platforms, including web, mobile, wearables, and smart devices, among others, and getting them to perform consistently is increasingly becoming a challenge. In 2026, automated testing platforms use cloud-based infrastructure to execute thousands of devices and browser combinations of tests at once. This scalability enables teams to test concrete user experiences in the real world, without having to run physical device laboratories. Visual testing tools are automated to compare the UI layouts across the devices to identify discrepancies and performance testing is done to ensure that apps are responsive to different network conditions. The outcome is a more credible and inclusive user experience in different environments.
Security and Performance Testing Integration:
The functionality is not the only aspect of quality assurance in 2026. The QA process is now automated with security testing. Vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues are automated and detected during the development of the tools. Organizations minimize exposure to breaches and regulatory sanctions by detecting security threats in time. There is also the development of performance testing. Rather than having performance monitoring confined to pre-release phases, the monitoring is performed after release. The automated tools replicate the actual user traffic, identify bottlenecks, and present information regarding the scalability problem. This constant validation makes sure that applications do not crash even with the increase in the number of users.
Collaboration and Reporting Through Smart Analytics:
The automated testing tools do not produce raw test results, but detailed and actionable insights. State-of-the-art dashboards show the trend, bring to the fore the issues and demonstrate the relationship between defects and update particular codes. Such an evidence-based model aids groups in making evidence-based decisions and giving priorities to improvements. Teamwork is improved with the help of shared reporting and real-time notifications. The same insights are reachable to developers, QA engineers and product managers to work towards the same quality objectives in the organization. The automated documentation also minimizes the manual work, which guarantees transparency and traceability during the development lifecycle.
The Human Role in the Automated QA Future:
Human expertise is still necessary despite the emergence of automation. Automated testing is very good when it comes to consistency and scale and human testers still possess creativity, intuition, and understanding of the context. QA professionals are concerned with the design of intelligent test strategies, assessment of user experience, and leading automation activities in 2026 to align them with business objectives. This development transforms the QA position to a leadership position. Quality assurance develops into a strategic operation that has a direct bearing on customer satisfaction, brand image, and success in the long term.
Conclusion: Building Quality into Every Release:
Improved intelligence in automation, constant test, and automated integration into the development lifecycle characterize the next generation of quality assurance. In 2026, automated testing will help organizations to work faster and provide more reliable and secure software. The adoption of AI-driven tools, shift-left, and scalable testing infrastructure will allow the businesses to make quality not a byword but a characteristic of any release.
With the software still determining the way people live and work, quality is the final differentiator. Companies that invest in advanced types of automated testing are not only enhancing their development process, but they are also future-proofing their products to meet the needs of tomorrow.
The Role of Generative AI in the 2026 Software Development Lifecycle
The development of generative AI has grown to be a fundamental aspect of software development in a very brief amount of time. One of the points where AI-assisted engineering will not be optional is 2026, which will be considered the basis of delivering in less time, achieving a higher level of quality, and making collaboration smarter. AI is being applied by developers worldwide to write code, identify bugs, test automatically, and even assist in making architectural decisions. Rather than substituting human inventiveness, AI is enhancing it, and software teams are creating overly dependable applications as never before.
The change is re-conceptualizing the software development life cycle (SDLC). Manual-intensive workflows that relieve manual effort are now complemented by AI models that are able to make suggestions in real-time, provide insightful information, and automate on every level. The outcome will be a new type of development environment where productivity is improved, the number of errors is reduced, and the teams will be able to pay more attention to innovation.
AI-Assisted Coding: From Autocomplete to Co-Development
Not too long ago, AI solutions could offer only basic autocomplete requests. These devices developed into completely interactive coding companions in 2026. Generative AI models are aware of programming logic, frameworks, and a real project. They are able to write full functions, create boilerplate skeleton and performance/security tune existing code. Developers would now start developing by stating intentions using natural language. The code is then written by the AI, and the developer reviews and amends, and instructs improvements. This joint venture accelerates implementation tremendously, particularly in repetitive or elaborate patterns. In the case of junior engineers, AI can be used as a guided learning tool that allows them to learn the best practices and minimize knowledge gaps. More to the point, AI can be used to ensure the consistency of large projects. It implies naming conventions, imposes patterns of architecture, and emphasizes non-conformity to the project standards. Rather than wasting time cleaning up the structure, developers can work on other aspects of the system and be able to resolve actual issues.
Automated Testing Becomes Intelligent and Predictive:
Testing is one of the SDLC phases that has always been time-consuming. Generative AI is changing this by automating the creation of tests and assisting the team in revealing the weaknesses earlier on. AI models are able to examine requirements and generate test cases to cover edge conditions and run them automatically in environments. This will be much more accurate, particularly in finding the weak points or performance bottlenecks. Predicting where bugs will occur before users see them, AI-driven tools detect bugs based on historical data on failure patterns and code by comparing these patterns. Maintenance testing is also faster.
Once a new update is applied to the codebase, AI is able to calculate which tests require rerunning to eliminate unneeded work. QA teams can peruse through prioritized results instead of sorting through thousands of test scripts, with root cause explanations. The end result is not only quality testing, but it is a smarter, more robust product.
Faster Debugging and Smarter Code Reviews:
The process of debugging has been said to be the most exhausting aspect of development. That burden is taken off in 2026 by AI tools. They recommend specific corrections based on the existing application logs, dependencies, and code history. Rather than having to manually trace lines of error, the developers are guided in reasoning and options for resolving errors. In a similar manner, real-time AI-promised feedback is added to the code reviews. The system brings out vulnerabilities in security, anti-patterns, and performance risks at an early stage, before the code is sent to the review stage. In the pull requests, the AI suggests ideas in context, why a code line is not working, how the code can be rewritten to run more efficiently, and should change should affect other modules. It minimizes the back-and-forth communication, shortens the review periods, and improves the quality of the code throughout the whole release process. The old senior engineers are now able to concentrate on the effects of strategic reviews and not syntax and formatting.
Collaboration Reinvented: Shared Intelligence Across Teams
Generative AI can boost teamwork by providing a knowledge-sharing platform that is open to all members of the team. Actionable insights can be summarized instantly in documentation, data models, architectural diagrams, and sprint histories. Team members can query the AI to get the correct knowledge about the project instead of spending time scrolling through long wiki pages or searching through old design files; thus, onboarding will become easier, and cross-functional collaboration will be much more convenient. The AI is considered a neutral communicator within distributed development setups. It assists in rewriting ambiguous requirements, documentation translation into other languages, and aligning the product objectives with the engineering decisions. Elements of miscommunication that could slow progress were previously detected and fixed automatically. Moreover, the developers in various time zones can leave the updates generated by AI to their colleagues, which means that the momentum will not be lost during the handoffs. The geographical limit, level of experience, and mode of communication do not restrict collaboration anymore — all people are equal in sharing the same level of intelligence.
Smarter Deployment and Continuous Improvement:
Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are increasingly complex, and the use of AI introduces automation and accuracy to the deployment processes. It anticipates the operational risks, forecasts the deployment time, and suggests rollback plans in case a release can lead to instability. One more feature of generative AI is ongoing performance monitoring in case an application is already online. It identifies anomalies and proposes specific remedies through real-time analytics, which sometimes identify a problem even before a user realizes it. The system continues to enhance its monitoring intelligence by studying the behavior of the applications over time. This proactive mode makes the response quicker in case of an incident, enhances the uptime, and safeguards the trust of the users.
Empowering Creativity Instead of Replacing Humans:
One of the most widespread mistakes is that AI is supposed to substitute for developers. The reality in 2026 is the complete converse. Repetitive tasks and those that are error-prone are handled by AI to allow human talent to work on innovation. The developers use less time on boilerplate code, rewrite cycles, and manual research, and more time to create unique features, improve user experience, and address real-world problems. There is also experimentation in AI. Engineers are able to prototype fast, experiment with the architecture, and receive feedback in real time. Projects that used to be conceptualized over a period of months are now developed in the course of weeks. The process of development becomes more enjoyable, educational, and creatively satisfying.
Ethical and Security Considerations in AI-Driven Engineering:
Although generative AI helps to boost development, it also comes with new obligations. The teams have to attentively watch the usage of the sensitive data by models and make certain that the models follow the rules. Code generated by AI should be checked to eliminate potential undisclosed vulnerabilities or licensing issues. Man, control is necessary in all stages. To use it responsibly, there must be transparency; developers must know why the AI made some decisions, not to accept the answers blindly. To put it in brief, AI simplifies development, yet the professional judgment ensures its safety.
Conclusion: A Future Where Humans and AI Build Together
By the year 2026, AI will have completely transformed software development, implementation, and improvement. The development teams will work more quickly and with fewer mistakes, and the testing will be predictive, and the collaboration will run smoothly with common knowledge systems. The SDLC has grown smarter, automated, and user-friendly for the developer.
Software engineering is not about humans and machines, but the future of software engineering is about people with some power over machines. With generative AI, developers gain productivity and complexity reduction and are free to do what they best imagine, design, and create amazing digital experiences. Those firms that adopt such a change today will be the pioneers of the new era of innovation as they create a world where technology constantly changes with potential and not restrictions.

The State of UI/UX in 2026: Designing for the Future
With the changing technology comes the expectation of users having to interact with the technology in their day-to-day activities. The year 2026 is a significant change in how designers consider the user interfaces and experiences. Mobile applications, websites, and smart gadgets are no longer evaluated based on the beauty of their appearance; users require smooth operation, individual experience, and convenience that support each of them. The UI/UX is changing more rapidly than ever due to innovations in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), and smart wearables sectors. It takes more knowledge of human behavior, emotional attachment, and digital inclusivity to design for the future.
Minimalism Evolves: Clear Design with Deeper Meaning
The principle exceeds simplicity, and in 2026, minimalist design has been ruling the years. Designers understand that a clean interface need not be hidden; it should be made visible. Rather than deprivation of the visual features in favor of appearing modern, the choices in UI are based on clarity: the user must feel assured and instructed in every detail of the process.
Precise typography, spaciousness, and orderly design must be used; however, the focus has changed to intentional simplicity. Actions are significant here, which are micro-interactions. There are subtle animations that react to touch, scroll or hover, which give the user immediate feedback, making them feel like they are engaged with the system. This will help the cognitive comfort, which is the less one has to think to use a digital product, the better the cognitive comfort levels of the user are. The radical minimalism trend, which was formerly disparaged as sterile, has been coming more alive and human.
Hyper-Personalization: Interfaces That Adapt to Each User
Personalization has ceased to be a bonus functionality and has become the basis of contemporary UI/UX. The current users’ demand experiences are characterized by their personal needs, preferences, and behavior. As machine learning progresses, user interfaces can change according tothe situation: What does this user like? At what time of day do they work? What are their goals? These behavioral signals are employed by design systems to customize content, layout, structure, and interaction paths dynamically. Applications are not static anymore: instead of showing the same UI to all users, they can dynamically evolve:
- The content is reorganized according to the most clicked.
- Recommendations vary on the basis of past activities.
- Navigation shortcuts are displayed on popular features.
This makes the interface look more relevant and gives a more emotional touch to the user. Nevertheless, the process of personalization should never violate privacy and data ethics – transparency and user approval are critical security measures.
Emerging Standards in Accessibility and Inclusive Design:
In 2026, the concept of accessibility ceased being a checklist point or a legal mandate – it is a fundamental experience principle. The designers have realized that accessibility has some positive effects on all people, including those without disabilities. Elements such as high-contrast themes, text scaling, closed captions, and voice interactions make it more comfortable for the general audience as well as accommodate users with various visual, auditory, and physical challenges. Laws in various locations have now been broadened to include inclusive design on all significant digital products, which prompts UX teams to reconsider their processes. The testing of accessibility is placed among all the design sprints instead of being placed at the end.
The device such as AI-based simulations of screen readers and automated usability testing can be used to identify areas of concern earlier. Emotional availability is becoming significant too. Interfaces have been designed to accommodate neurodiverse users with too few things that can overwhelm them, decreased cognitive load, and predictable patterns of interaction. The future of UI/UX is made to suit all types of minds, not only that of the average mind.
Immersive Experiences: AR and VR Become Mainstream UX Tools
The development of AR and VR technologies has opened up an absolute world of new dimensions in design. The immersive interfaces are no longer restricted to games in 2026, the interface is influencing retail, education, health, and work inter-relationship. AR is the digitization of information that is superimposed on the real world and allows users to communicate with apps in their daily activities. There is interaction in the shopping experience; the customer is able to visualize the furniture in his or her home before he or she buys it. The navigation applications show real-time routes on the sidewalks. Through educational tools, 3D models are introduced into the learning environment of students, and they make learning discoveries.
Virtual reality is turning into a training, remote working, and socializing platform. The skill set to design for VR is a totally different spatial interaction, motion sensitivity, depth cues, and gesture controls that are intuitive and replace the touchscreen behavior. The designer of 2026 has to be cross-disciplinary: a storyteller, an animator, and a usability engineer.
Immersion presents difficulty, as well. The environments that are overstimulating may cause discomfort, particularly in first time users. The key to the future of immersive UX will be balance, or experiences that are both magical and at the same time, effortless, accessible, and comfortable to touch.
Voice, Gesture, and Touchless Interaction:
The trend of moving to hands-free interfaces is not slowing down. Home appliances, vehicles, and wearable gadgets are ushering in emerging UX designs where people turn to voice recognition or physical gestures instead of touching screens. The processing of natural language has advanced to the extent that voice commands can be conversational and very adaptive. Gesture-based design is slowly growing with motion sensors and haptic feedback. This multi-modal form of interaction acknowledges that users are frequently multi-tasking in driving, cooking, exercising, or walking. Interfaces in the future should be able to react with ease to various situations without the need to receive visual attention. To designers, this changes the UI work into the way conversations and behaviors are shaped rather than buttons and icons alone.
Data-Driven Design and Ethical Responsibility:
All UX decisions made in the present-day are affected by analytics – heat maps, A/B tests, session recordings, and sentiment scores. Data can assist teams to not only know what users are doing but also why they are doing it. In 2026, the move towards data-oriented design promotes constant enhancements: products will improve as users act, as opposed to extended intervals between product redesigns. Ethical responsibility is, however, of great concern as personalization and analytics get deeper. The designers should avoid manipulative patterns, honor user autonomy, and avoid dark UX practices, which deceive people into doing something they do not want to do. The element of trust has become a very important element of user experience. The most effective products are those that process data in a transparent manner, safeguard privacy, and prioritize the well-being of the user in each and every decision.
Future-Ready Design Systems: Flexible, Scalable, Consistent
UI needs to be flexible as digital platforms are rolled out on more devices, such as smartphones, foldables, TVs, AR glasses, and smart car dashboards. The 2026 design systems are made by components which get fluidly larger in size, shape, and complexity. These systems are consistent and can be customized to many settings. The UX teams do not design individual experiences per screen but rather design modular systems that are usable in any location. The method accelerates growth, enhances brand awareness, and ensures accessibility criteria among ecosystems. The outcome is a cohesive experience that becomes familiar regardless of the way the user handles it.
Conclusion: Designing With the Human Future in Mind
The UI/UX state of 2026 is based on a radical transformation: technology becomes less technical, more human, and can be considered emotionally sensitive. Interfaces are not fixed screens anymore – it is a dynamic environment, which follows a user through their day-to-day life. Design needs empathy, creativity, and multidisciplinary thinking in the future. Designers have to know psychology as well as they know images and code. They need to anticipate not only user clicks, but also their emotions, studies, and social interactions as well. With the continuous growth of AR, VR, AI, and new devices, the most successful experiences will be the ones that will enable users but not overwhelm them. The future of designing is not a pursuit, but a move towards creating digital realms that are accessible, intelligent, and genuinely human-centric in 2026. The future of UI/UX lies with those who design outside the screens and think outside the box.

Case Study: How We Helped a Mid-Sized Company Optimize Their Mobile App’s Performance
Customers of mobile devices now require convenient, high-speed digital experiences. Any sluggishness or technical problem will instantly affect their confidence and loyalty. This is precisely what happened to a mid-sized consumer service company, otherwise known as BrightPath Services, before they became our partners. Its application was necessary to enable the customer to make an appointment, follow up on the changes, and reward. But the performance issues started to undermine the satisfaction of users and the brand’s trust. This case study describes the process of identifying the problems and providing a specific optimization plan as well as turning their application into a stable, high-performance product.
The Problem: Slow Performance and Rising User Frustrations
BrightPath had already spent a lot developing apps, yet the number of user complaints started to grow. The issue of long loading screens, frequent crashes, and feature-to-feature freezes was not easily overcome by the customers. Particularly, these problems were more problematic on older devices, which constituted a significant percentage of the user base. The rating of app stores went down to 3.1 stars instead of 4.4, and over 40 percent of new users discarded the app after the first use. The number of technical complaints filed by customer support teams and the marketing department even stopped promoting the app in case of a negative public response. Internally, the company started doubting the fact that the app was turning into a threat rather than a strategic asset to the brand.
Our Diagnostic Approach: Data Over Guesswork
To find the real reasons for the decline, our team has performed a comprehensive performance audit. This involved real device testing, back-end testing and crash analysis, and studying the user behavior data. The results showed one to be a mix of unseen backend inefficiencies as well as visible user experience barriers. The rendering was slow because of heavy images and unoptimized UI elements. The API calls were cumbersome, which made the loading time and transition to be slow. The old software elements caused spontaneous crashes. The onboarding process of users was also accompanied by a series of slow processes, which made it frustrating. This was a summary of all these problems, and it was like the users were being chased away rather than embraced.
Strategic Solution: Rebuilding Speed and Experience Together
Having a precise diagnosis, we have devised a whole optimization strategy that would be focused on speed, stability, and usability. At the end, we refactored on our UI elements to make them more efficient and added lazy loading to make sure that only critical content was loaded initially. Media data was also made smaller to lessen the load on gadgets without compromising the quality of the image. On the server side, we optimized the database and API communication to make the responses quicker and shorter during navigation. With high-quality debugging tools, we were able to find some memory leaks that made the app crash on lower-RAM devices, fixing them gave us significant stability improvement. Concurrently, we redesigned the onboarding process. We did not make users scroll a couple of screens, but provided an easier and more intuitive interface that loaded almost immediately. Lastly, we introduced automated monitoring tools to notice performance decline at the earliest stage and equipped the inner team of the client with better coding standards to be sustainable in the long term.
The Results: A Faster, Stronger, More Engaging App
These benefits were not only short-term but quantifiable as well. There was also more than a 50% reduction in the time taken to launch the app, and this enhanced the very first impression of the product by the users. The crash rates were reduced to less than 1 percent as compared to more than 4 percent, and this made the app much more reliable. The retention of users rose by over 35 percent in 3 months, and conversion on critical features, booking action, purchasing action, among others, rose by nearly 30 percent. Most remarkably, the application store rating improved once again to 4.5 stars as the positive feedback overtook previous complaints. The customer support team can be able to work on more significant service interactions with fewer performance-related tickets. Confidence in the market was restored and succeeded in the promotional campaigns and adoption. The app took a turn to become an unsuccessful asset and a strong force to drive customer engagement and increase revenues.
Client Satisfaction: A Turnaround That Inspired New Confidence
The turnaround was a relief and a win for leadership at BrightPath. They referred to the change as a restoration of both the functionality of the app and internal faith in its strategic worth. They observed that our close working style, coupled with the transfer of knowledge and constant check-up tools, made their teams feel more empowered and capable of continuing with the improvements on their own. The restored user confidence was vividly reflected in the reviews of customers, which described speed, ease of use as well and reliable performance.
Key Insights: Performance Optimization Never Stops
A great lesson that I learned during this project is that it is not a one-time thing when it comes to performance. Mobile ecosystems are dynamic and keep changing, as new devices are being added into the market, new operating systems are being released periodically and usage patterns are changing as well. Even applications that are well-developed deteriorate without maintenance. That is why we assisted BrightPath in building a long-term performance governance with regular dependency updates, stress testing, and automatic alerts for early issue detection. The company will be in a better position to continue providing the same experience that customers expect because it has transformed optimization into a continuous process.
Conclusion: Turning Weakness into a Winning Advantage
The experience of BrightPath Services demonstrates how fast an online product may fall behind in case performance problems remain unaddressed – and how effective the recovery can be when the correct approach is chosen. Customers react by being loyal and engaged with an app that upholds their time with speed and reliability. However, the optimization of performance was not just a technical solution, but it also rebuilt the confidence of the market, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased the growth opportunities of the company in the future. It is worth noting that the mobile app of BrightPath is a good brand promise today. The fact that they have succeeded confirms that all the struggling apps can be changed with the help of data-driven decisions and experience-based improvements.

Data-Driven Decision Making: Your Competitive Edge
In the digital transformation era, data is now the richest asset to contemporary organizations. Any interaction, whether it is a click on a web page or a purchase made, creates valuable insights that can assist businesses to know their customers, ease operations, and anticipate market changes. However, the actual competitive strength of data is not the quantity that the business gathers, but the strength of data analysis and utilization in making a strategic decision. With more dynamic industries and uncertainty being the new factor of existence, data-driven decision-making has become the sole way of remaining agile, creative, and future-ready.
Companies that operate under pure intuition risk making obsolete decisions or biased decisions. In the meantime, institutions that base their strategies on data are in a better position to be able to adapt fast, find new opportunities, and reduce risks. Startups, big businesses, and everything in between: the capacity to convert data into meaningful intelligence has become a make-or-buy decision when it comes to attaining sustainable growth.
Why Being Data-Driven Is Essential for Modern Success:
The expectations of customers have been raised incredibly high. Consumers insist on personalized, smooth, and effective communication with all the brands that they interact with. With effective data usage, firms are able to provide customers with precisely what they desire, at a time they desire, and in the medium that they desire.
The benefits extend way beyond customer experience. Data analytics enhances decision-making at all levels:
- Leaders have real performance visibility and can respond faster.
- Marketing departments make campaigns optimal through real behavior.
- Product teams enrich innovation with feedback trends.
- Finance departments are more precise in revenue and risk management.
- Operation teams eradicate inefficiencies and expenses.
All the departments are better when the decisions are not made based on assumptions and conclusions. The latter makes data-driven organizations stronger and more competitive in general.
How to Build an Effective Data Analytics Strategy:
To become a company that is data-driven successfully, it takes a well-organized and considered strategy. It starts with setting the right goals. The outcomes that a business is interested in — such as improving conversions, increasing loyalty, or internal productivity should be supported by data. Considering that objectives are clear, analytics may serve as a reporting tool but also as a growth driver.
The next thing that follows the definition of goals is the collection of relevant data. A large part of companies already possess valuable information that is distributed across various systems, such as websites, CRM systems, loyalty applications, social media, payment systems, and customer support systems. It is important to consolidate all this in a central, safe data platform. The use of cloud-based data warehouses and data lakes has become common as they enable teams to store, arrange, and retrieve vast amounts of structured and unstructured data without spending too much on them.
After creating the data foundation, it is recommended that businesses select analytics tools that enable the readily interpretable and usable insights. Analytics tools such as Google Analytics 4, Tableau, Power BI, Looker, and SAS can be used to convert complex data into dashboards and reports that are easy to understand. Artificial intelligence-based solutions can further extend to predicting and finding patterns that human beings would not have noticed.
Finally, it will eventually democratize data, making all departments access the information they require. Free flow of data in the organization leads to faster decision-making processes that are smart and focused on common goals.
Using Predictive Analytics to Drive Future Innovation:
The machine learning models examine the behavioral trends, the buying history, the seasonal trends, and the external factors to be able to make some informed predictions. This enables the businesses to be proactive in influencing the outcomes instead of responding to what has happened.
Take real-life examples:
- Retailers will be able to predict demand and manipulate inventory to avoid inventory shortages.
- Banks can identify early signs of fraud and impose greater security.
- Travel agencies are able to know when to expect large bookings and how to maximize pricing.
- Healthcare organizations are able to identify patients at greater risk and provide early action.
Predictive analytics transforms uncertainty into opportunity. When the businesses have an opportunity to predict what the customers would need or interrupt, then a strong competitive edge is achieved, which would not have been achieved through intuition.
Cultivating a Data-Driven Culture Across Teams:
It is people who transform a company, rather than technology. The level of data-driven culture helps to push employees towards using insights and to demonstrate the old decision-making practices. Once teams believe in the numbers and have a feeling of how to interpret them, then data will become a communal asset that drives teamwork and creativity.
Leadership is very essential in developing this culture. Executives should be the first to provide guidance in their organization by using analytics to make their decisions and report performance in an open manner. The employees can be provided with training programs to gain confidence in interpreting dashboards and deriving meaning out of reports. The better acquainted the staff is with data, the smarter the staff can be in solving problems to achieve positive results.
It is also important to promote curiosity. When workers are given the freedom to seek trends, challenge assumptions, and experiment with evidence, the company will be more flexible and innovative.
Enhancing Customer Experiences with Deeper Insights:
Each customer interaction leaves a digital footprint – and the study of the footprints can be truly insightful. Businesses are able to know what customers adore, where they become frustrated on a website, or why they leave their carts before they complete the checkout.
Using modern analytics, businesses will be able to trace the journey of different customers and streamline all stages:
- The ability to personalize the content of the websites to suit the interests of the users.
- Personalization of product suggestions through the history of browsing.
- The provision of focused marketing communication messages at the ideal time.
- Feedback analysis to improve the quality of services.
With the new norm of personalization, customers are attracted to fasten themselves towards the brands that make them feel special and appreciated. Information gives organizations the ability to deliver experiences that are beyond expectations on a regular basis.
Operational Efficiency Through Intelligent Data Use:
There is also the transformative impact of analytics in the background. The companies will be able to track the processes within the company in real time, detect inefficiencies, and enhance productivity. Indicative of this, in case of machines, IoT sensors help the manufacturers to identify their wear before they malfunction, saving thousands of dollars in repair fees. To make deliveries faster and less costly, logistics firms study the routes to travel and consumption of fuel. Operational Intelligence enables the organization to go to market quicker, incur less expenses and outperform firms that depend on the workflows of yesterday. It is natural and continuous when all processes can be measured, which means that their improvement is possible.
Maintaining Trust with Ethical Data Governance:
Due to the increased significance of data, the ethical responsibility of managing it increases as well. Customers demand transparency – they need to be informed what information is being gathered, and how they will use it. Developing robust data governance systems safeguards privacy and creates trust. Encryption, identity access control and adherence to regulations e.g. GDPR is one of the security measures that ensure that sensitive information is secured. When companies show integrity in data management, clients will be more ready to provide information – driving even deeper analytics solutions.
Measuring the Impact: Proving ROI with Analytics:
An effective data-driven plan has quantifiable results. Some of the KPIs that businesses need to set to measure the value of analytics initiatives include:
- Improved conversion rates
- Higher customer retention
- Reduced operational costs
- Increased revenue accuracy
- Reduced time to make decisions.
The ability to show real gains will allow businesses to invest more in analytics and ongoing innovation.
Conclusion: Winning the Future with Data-Driven Strategy
Information is changing the nature of competition and the success of organizations. It is the companies that adopt analytics that are able to find new market opportunities, get to know customers better, and solve issues before they get out of control. Decision-making based on data not only enhances performance but also boosts growth. With the business environment growing increasingly unpredictable, the most intelligent plan is the one that will be created with insight, flexibility, and evidence. Those organizations that believe in data-first thinking will be ahead of the pack in their industries and others will not be able to follow them.

Leveraging Machine Learning to Enhance Customer Experience
Introduction: Transforming Customer Experience with Machine Learning
Customers in the digital-first world of 2026 want their brands to know them and their needs immediately, know what they like, and serve them at a level of personal precision. They are no longer sensitive to generic marketing messages and slow services. Rather, they desire highly personalized, smart and smooth experiences in all interactions both online, mobile, and in-store.
Machine learning (ML) is one of the most influential branches of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows computers to improve autonomously and learn based on information. Unless it specifically mentions so, businesses are using ML to study behavior, understand intent, and customize every customer interaction point in its customer journey.
This paper discusses the importance of machine learning in improving customer experience (CX) by personalizing, predicting, and automating as well as ensuring ethical and data-driven customer interaction in the age of intelligent business.
The Role of Machine Learning in Customer Experience:
Machine learning can assist businesses to transition into the proactive customer engagement. Companies are able to predict behaviors and anticipate needs before the customers even request something rather than responding to what customers say or do.
Fundamentally, ML can recognize trends in huge data sets like history of purchases, browsing history, and log of interactions to predict or make recommendations accurately. These lessons can assist businesses to provide context-sensitive experiences that are effortless and natural.
ML algorithms can, in a particular instance, recommend items that a user is likely to purchase, identify dissatisfaction in a voice or text, or automatically respond to support replies in real-time. The outcome is a more seamless, intelligent, and more human experience that is driven by data.
Personalization at Scale: Turning Data into Human Connection
Personalization has developed much beyond including the name of a customer in an email. Machine learning supports real-time hyper-personalized experiences that are responsive to individual user preferences and behaviors in large scale.
AI-Driven Recommendations:
ML-powered recommendation engines have transformed business products or service suggestions. Such systems are used to predict what users will love next based on past behavior, demographic information, and contextual information by platforms such as Amazon, Spotify, and Netflix.
This works as well to enhance engagement and loyalty and the customers are not being sold to but they are being understood.
Smarter Marketing Campaigns:
Conventional marketing segments the audiences. Machine learning goes even further and does this at the level of creating segments of a single. The ML algorithms examine the open rates, browsing history, and time of engagement, and use them to dynamically customize messages.
As an example, when a user is a regular sportswear shopper, the algorithm will ensure that they get real-time deals on sportswear that they are interested in and the conversion rates increase.
Dynamic User Interfaces:
Machine learning has the capability to adjust digital interfaces in real-time. E-commerce websites have the ability to move the product categories or show the promotions depending on the behavior of the individual visitor. This implies that each user perceives a site or an application that is designed to suit their individual experience.
Personalization enables brands to build emotional relationships, making each contact with a customer feel special and important under the influence of ML.
Predicting Customer Behavior with Data Intelligence:
Predictive analytics is a machine learning-driven system that helps companies to predict customer behavior before it arises. Through pattern analysis and historic information, the business can detect opportunities, avoid problems as well as make evidence-based decisions promptly.
Reducing Customer Churn:
Churn prediction is one of the most useful ML services in CX. Customer-at-risk algorithms have the potential to identify at-risk customers by identifying early warning signs, which can include decreased engagement, increased response time, or negative feedback.
With this understanding, companies can make proactive moves, providing discounts or personalized attention to customers before it is too late.
Demand Forecasting:
It is possible to predict the sales trends, seasonal demand, and fluctuations in the market with great precision using machine learning models. This makes sure that the businesses have optimum inventory and that there is no shortage of products, and products are given at the time the customers need them the most.
Sentiment Analysis:
Using Natural Language Processing (NLP), ML systems are able to understand the emotions of customers in social media posts, reviews, or even in a chat. They recognize the tone, spot the dissatisfaction, and assist companies in responding both empathically and promptly.
Such insights help brands to make products better, educate the support team, and build relationships with the audience.
Predictive ML models transform data on the customers into foresight that gives a brand the ability to predict needs and respond accordingly.
Automating Customer Support with Machine Learning:
Customer service has been revolutionized by AI-powered automation by turning it into a problem-solving mode of customer support for an active service. Machine learning makes operations simpler, it lowers the response time, and improves the consistency in communication.
Smart Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Chatbots nowadays are not based on fixed scripts. They perceive intent, context, and even feeling using machine learning and NLP.
Bots such as ChatGPT, Alexa, and Google Assistants, which can be used as virtual assistants, have established a new benchmark of conversational artificial intelligence. Custom bots are used by businesses that:
- Give immediate responses to frequently asked questions.
- Troubleshooting users.
- Refreeze complicated problems to human agents where needed.
This combination model will provide speed and empathy in customer care.
Anticipated and Automated Routing of Tickets:
Machine learning is able to automatically categorize customer tickets based on urgency, topic or sentiment and direct them to the right team within seconds. This increases the time that is resolved, and high-priority cases are given priority to be addressed.
The proactive service that is predictive in maintenance:
ML models have been used in real-time monitoring of the performance of products in automotive and manufacturing industries to foresee and prevent failures. As an illustration, smart devices and appliances will be able to notify users of maintenance requirements, enhancing reliability and brand loyalty.
Automation not only boosts efficiency, but it also increases empathy by having the capability of responding promptly and intelligently to all customers.
Enhancing Customer Journeys with Real-Time Insights:
The current customer experience takes place across a series of channels, including web and mobile applications, chat, social media, and brick-and-mortar locations. Machine learning brings these touchpoints together as a single smart ecosystem, which helps brands to provide consistent, contextual experiences.
ML models are anticipated to respond to the cross-channel behavior in order to understand the location of the customer on their path and the next action that is most likely to be taken by the customer.
For example:
As an example, a consumer checking an online store may then see a customized advertisement of that product on social media later that day.
- It may happen when a mobile banking app provides a customized loan application in accordance with previous transactional information.
Connecting behavioral data between channels allows the business to make sure that each interaction, regardless of the location, feels like one continuation.
Responsible and Ethical AI in Customer Experience:
Ethical implications should be kept at the top, as machine learning is being more integrated into CX. Customer relationships are based on trust, and mismanagement of data will undermine the trust within a short time.
The concept of responsible AI is to be truthful about the use of data, not to be biased with algorithms, and to guarantee user privacy.
In order to develop trust and adhere to international rules:
- Get explicit customer permission for data collection.
- Fairness and accuracy: Audit ML models on a regular basis.
- Explain the decision-making process using explainable AI (XAI).
- Enforce powerful encryption and anonymization laws.
Compliance is not the end of ethical AI; an ethical AI helps to keep your brand intact and earn loyalty by being transparent.
Real-World Examples of ML-Driven Customer Experience:
Major brands have already shown the way in which ML can transform customer experience:
- Netflix uses ML to offer personalized recommendations to users on what to watch, maintaining high levels of engagement.
- Starbucks employs predictive analytics to suggest person-drink combinations in its mobile application.
- Sephora uses AI-based virtual try-ons to allow customers to envision the products and purchase them.
- Delta Airlines is a company that makes use of predictive models to enable it to rebook its passengers in advance who have been delayed in their flights.
These stories of success demonstrate that machine learning not only streamlines operations but also builds an emotional bond by making the experience of customers more seamless, quick, and personalized.
Creating a Machine Learning Strategy to achieve Excellent CX:
A strategic roadmap is needed in the organization that intends to maximize customer experience with machine learning:
- State your mission: Determine where ML can be applied: personalization, support, or retention.
- Gather quality data: Convert data between touchpoints and clean it to send to accurate models.
- Choose the appropriate tools: ML frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Google AI will give you flexibility.
- Integrate and automate: Link ML to CRM, marketing, and analytics systems.
- Measure and evolve: monitor model accuracy, customer feedback, and KPIs continuously to improve with time.
An effective ML approach to the matter is not merely about technology but rather about human insight and smart systems to produce valuable customer impact.
Conclusion: The Future of AI-Enhanced Customer Experience
The concept of connecting with customers is being redefined by machine learning. Hyper-personalized experiences to predictive service and intelligent automation. Hyper-personalization and predictive service: ML helps brands provide an experience that is effortless and intuitive.
In the future, 2026 and beyond, companies that use machine learning will not be distinguished by the volume of data they accumulate, but by the level of their intelligent use. The future is with organizations that merge data science with empathy, with the help of AI, not only to sell, but to serve.
Machine learning not only improves customer experience, but it also makes it a living, dynamic relationship between smart systems and humans.

Planning Your 2026 Website Redesign: What You Need to Know
With the world becoming digital at a very fast rate, companies are realizing that websites that were developed a few years ago are no longer suitable in the current times. By the year 2026, the behavior of the users, the type of device, and the level of performance will all have changed to a new level. Consumers have become in demand of websites that are aesthetically pretty, rapidly responsive, and those that can offer a tailor-made experience once they open a page. When a site seems old, slow to load, and unable to capture the attention of visitors, it can lose its credibility and presence in a competitive market.
A redesign in the modern world is not simply a matter of updating the appearance of your site. It is a chance to update your brand image, use the newest technologies, enhance your SEO base, and make your experience more intuitive to your audience. As the design trends and web structures develop and evolve at an impressive rate, 2026 is an ideal time to reconsider your online presence and create a platform that will be able to sustain your business in the future.
Modern Web Design Trends Shaping 2026 Redesigns:
The 2026 web design will be motivated by the combination of clarity, immersion, and user control. Content-first and minimalist layouts remain dominant as these provide a chance to help the visitor concentrate on what is important and remove any distractions. Simple navigation, clean spacing, and high visual hierarchy provide a space in which the important information is in your face, and the users do not waste time trying to see what they are interested in.
The other important trend is the emergence of immersive visuals. Shorter videos, dynamic illustrations, micro-animation, and slight transitions are added to websites, which make the online experience look slick and interesting. Micro interactions Micro interactions, or small animations that are triggered when a user hovers, scrolls, and clicks, are fundamental to interfaces and make them seem living. Such additions not only provide a personality, but they also direct the attention of the user to the website in a meaningful manner.
Personalization is also getting to be standardized based on AI. The use of modern websites adapts the content dynamically depending on the behavior of the user, past usage, localization, and interests. Your site becomes a smart, responsive system, and instead of delivering a single experience to all your visitors, it delivers an appropriate message at the appropriate time. Together with that, dark mode options, high-contrast themes, and accommodating visual design solutions make users feel more at ease without compromising on the accessibility of the website to people with various needs to view it.
Prioritizing High Performance and Multi-Device Responsiveness:
Performance of the websites has taken center stage among the factors that matter most in the redesign process. Slow loading speed is no longer tolerated by users; when it takes too long before your content can be loaded, they just move on to a site that loads faster. Performance is now directly related to visibility and conversion rate, with Google Core Web Vitals affecting the ranking of searches. In 2026, websites should be fast across both the elderly and slow networks of mobile devices, and should load assets such as images, scripts, and videos to reduce delays.
The area of responsiveness is changing as well. No longer is it sufficient to serve desktops and mobile, but websites have to serve foldable phones, the ratio of tablets, ultra-wide screens, smart televisions, and new form factors every year. A contemporary redesign is one that makes all the contents, such as the navigation menus, interactive graphics, etc., capable of adapting to the size of the screen that the user is using. It provides a unified device experience and alleviates the frustration caused by stale and strict page designs.
To perform at this scale, most redesigns have included faster frameworks, headless architecture, and static site generation and deployment on the cloud. These technologies help to make your site simpler to scale, safer, and able to deliver content to users virtually instantly, no matter where they may be across the globe. Blended with CDN caching, new compression algorithms, and clean code habits, your new website is a potent tool created to run fast and stable.
Building a Strategic Redesign Plan That Aligns with Your Business Goals:
The redesign of the 2026 website will commence a long time before the graphics are produced. It begins with an in-depth analysis of what is functioning in your existing location to find out where you have problems and where the users are having trouble. This involves the examination of loading speeds, a heatmap study, evaluation of engagement metrics, monitoring the health of the SEO, as well as determining stale parts of the content. It is our foundational research that will guarantee that your redesign is founded on data and not speculation.
The second move is to establish specific objectives for the redesign. You might wish to boost lead creation, user navigation, modernize brand images, enhance your search engine presence, or venture into new locations. Whatever the purpose, it will inform you of all the future design and technical decisions. In the absence of this articulation, redesigns may appear beautiful to the eye but will not achieve any meaningful business impact.
It is at this stage that user journey mapping is necessary. Knowledge about the flow of visitors on your site including where they land, what they seek, and the steps they have to take before they leave their path will be used to design the layout of your new site. Redesign, with a focus on the user’s needs, is more instinctive, more compelling, and more adjusted to the customer’s expectations.
The selection of the appropriate platform and development strategies is also significant. Certain brands can be developed entirely custom, and some can be developed with flexible CMS systems such as WordPress, Webflow, Sanity, or headless systems which decouple design and content management. The proper choice of technology would make sure that your redesigned site not only appears modern but is scalable and can be easily updated by your staff without the need to reiterate the development process.
Crafting Future-Focused Content and Ensuring Accessibility:
Redesign is the ideal occasion to renew your messages and improve the level of content. You will have to rewrite content, so it sounds like your brand and reflects your current services and supports your new navigation and structure. It is also to be optimized in terms of search engine optimization using key strategic words, eye-catching headings, and interesting stories that keep the users engaged. Rather than just aiming at carrying the old material and putting it in a different layout, the redesigning process challenges you to reconsider what your audience values and what the most appropriate manner is to convey that value.
Another important element of contemporary web design is accessibility. Inclusive design is not a choice anymore as global regulations are reinforced. A professional redesign makes sure that it is compatible with screen readers, logical navigation by keyboard, properly labeled images, high-contrast images, and clear typography. This pledge enhances usability and builds trustworthiness to all users and also increases the credibility of your brand since it demonstrates that you not only care about all users but also about their ability as well.
Launching, Testing, and Maintaining Your Redesigned Website:
Rigorous testing is done once the new site is finished. This step entails the testing of the site on its various devices, browsers, and the types of screens. All the forms, buttons, animations, and interactive factors should work well. Speed tests, user tests, SEO audits, and accessibility checks make the site ready and polished.
Monitoring after the launch is also important. By tracking the engagement, conversion rates, behavior flow, and traffic patterns with the help of analytics, it will be possible to see how the users will respond to the new design. Such insights can help you to improve on areas that might need improvement and also make sure that the site keeps meeting the changing user expectations.
The redesign of your 2026 website must not be seen as an end in itself but as a beginning of a new digital age for your business. Routine changes, constant content development, seasonal updates, and constant optimization will make sure that your site remains topical and competitive in the continually evolving online world.

Essential Cybersecurity Protocols Every Business Must Implement Before 2026
Introduction: The Rising Urgency of Cyber Defense:
Cybersecurity has ceased to be a technical issue and is now a business survival issue as we approach 2026. As the number of cyberattacks increases in frequency, complexity, and cost, there is no organization, large or small, that can afford to rest. Later reports worldwide indicate that the average data breach cost in 2025 would be over $5 million, and due to the development of AI-assisted hacking tools, the cost will be a lot higher in 2026.
To the present-day businesses, cybersecurity is not a luxury, but it is a necessity. Whether it is financial data, healthcare records, or intellectual property information, it is important to put in place strong security measures, which will safeguard the image of your company, finances, and even customers.
This paper is a list of cybersecurity measures required in 2026 to ensure every business has taken the necessary actions to ensure the safety of its data, networks, and infrastructure in the dynamic threat environment.
1. Establish a Zero Trust Security Framework:
Zero Trust has become the new standard of cybersecurity of an enterprise. In contrast to the traditional security of the perimeter, in which it is discussed that a user within the network can be trusted, Zero Trust is based on the never trust, always verify. All devices, users, and network requests are verified and authenticated before access, irrespective of the source. This will reduce the lateral movement in case there is a breach and keep the sensitive systems segregated.
Key actions:
- Install multi-factor authentication (MFA) in all systems. •
- Isolate sensitive data environments by using micro-segmentation. •
- Take a constant check on the logs of access to see abnormal activity. •
- Make use of the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to provide access only as much as needed by the users.
Zero Trust is not merely a system, but also an attitude that offers rigorous access control and constant validation of your whole digital ecosystem.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere:
It is no longer possible to use passwords. One of the most effective, but also the simplest, methods of ensuring unauthorized access is multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA uses two or more forms of verification (Something you know (a password), something you have (a device), or something you are (biometric). Although a hacker may steal a password with the help of phishing or brute-force attacks, MFA is an extra security barrier.
Best practices:
- Insist on MFA on every employee account, including administrative and remote.
- Apply adaptive authentication based on the device type, location, and risk level.
- Install MFA in VPNs, email systems, and cloud service providers.
Descartes reveals that the MFA is capable of preventing more than 99% of automated cyberattacks, and it is one of the simplest to succeed in the current security environment.
3. Encrypt Data In Transit and at Rest:
Encryption will ensure that even when hackers intercept sensitive data, they will fail to read it, as the messages are coded in such a way that only the appropriate key will make them understand what it is. In the years to come, 2026, remote work and cloud computing will grow, which means that data encryption is essential at all levels of the digital journey.
Action points:
- Encrypt stored data with AES-256 and encrypted data in transit with TLS 1.3.
- Use end-to-end encryption of emails and messaging services.
- Frequently change encryption keys and apply key management systems at a centralized location.
- Make certain of complete disk encryption of laptops and mobile devices used by the company.
Encryption creates trust on top of compliance – customers and partners are more confident that their data is secure at any moment.
4. Periodically Change and Upgrade systems:
Hackers tend to take advantage of the existing software vulnerabilities that have not been patched. Actually, there were numerous high-profile breaches, which arose due to the businesses’ neglecting to use available updates.
Automated patch management is essential in 2026 when the software layers are sophisticated and decentralized. Constant changes seal the security gaps before they are exploited by hackers.
Recommendations:
- Automate updates on OS and applications.
- Keep a list of assets of devices, applications, and IoT systems.
- Test important patches in a sandbox before installing the patches.
- Use a patch with an important vulnerability within 72 hours.
Uniformity is the first step in cyber hygiene; though patching might sound boring, it is among the best defenses against breaches.
5. Secure Cloud Infrastructure and APIs:
With cloud adoption still prevailing in the business IT department setting, data leakage has mostly been a result of misconfigurations. Improperly implemented storage buckets, unprotected APIs, and insufficient IAM (Identity and Access Management) protection can be used as a backdoor to attackers.
To achieve cloud ecosystem security:
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools can be used to detect misconfigurations.
- Encrypt and log all assets in the cloud.
- Use hard IAM roles and a conditional access policy.
- Periodically scan API endpoints and rate limit to avoid abuse.
- Install Kubernetes and Docker workload container security solutions.
Security in the cloud is collective- your provider secures the infrastructure, but it is up to you to protect data, configurations, and access.
6. Enhance Endpoint Security and Network Security:
Remote work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) have made the remote work model commonplace, which makes each laptop, phone, and tablet accessing company data a vulnerability.
Install an Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) to track devices in order to detect suspicious activity. Combine this with Network Detection and Response (NDR) to get end-to-end visibility of your IT environment.
Key measures:
- Install some sophisticated antivirus and antimalware software.
- Use Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and firewalls.
- Implement the encryption of devices and automatic locking of screens.
- Divided corporate networks to restrict inter-departmental flow.
A secure network has a smaller attack surface, and potential threats are contained. F
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning:
No system is completely invincible, even with the best defenses. That’s why a robust backup and disaster recovery plan is essential for business continuity.
Since ransomware attacks often target the backups themselves, it is extremely important to maintain multiple, isolated copies of critical data.
Checklist:
- Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: 3 copies of data, 2 different storage media, 1 offsite copy.
- Test the recovery procedures regularly to ensure prompt restoration.
- Store one backup offline, air-gapped, to prevent ransomware encryption.
- Use immutable backups that cannot be changed or deleted.
Downtime can cost millions; regular testing enables quick and confident recovery when disaster does strike.
8. Conduct Employee Cyber Awareness Training:
Human error is still among the top causes of data breaches. Attackers continue to take advantage of phishing, social engineering, and weak passwords.
Regular cybersecurity awareness training will transform employees into your first line of defense. Educate staff on how to recognize phishing emails, good password practices, and incident reporting procedures.
Tips for Effective Training:
- Simulate phishing attacks to test employee vigilance.
- Update training modules with the latest trends quarterly.
- Encourage a “report-first” culture where employees should never fear reporting all potential incidents:
A well-informed workforce is just as important as firewalls or encryption: it’s the human shield protecting your digital assets.
9. Monitor, Detect, and Respond with Security Operations Centers (SOC):
By 2026, real-time threat detection will no longer be optional. Enterprises will adopt SIEM and SOC solutions that permit the effective monitoring of network activities to ensure quick reactions to deviations.
Modern SOCs depend on AI-driven analytics to pick out suspicious patterns before they escalate into full-scale attacks.
Core capabilities to include:
- Centralized logging of all system and application events.
- Automated Incident Response Workflows
- 24/7 monitoring with alerts for unauthorized access or unusual traffic spikes.
- Unified visibility via integration with EDR and NDR tools.
An active SOC converts cybersecurity from a reactive role to an active defense mechanism.
10. Comply with Regulations and Frameworks:
Regulatory compliance is both a legal requirement and a trust factor. Depending on your industry and geography, frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, SOC 2, and NIST define the standards for data protection.
Compliance with these regulations ensures reduced liability, enhanced transparency, and increased customer confidence. Perform regular audits for compliance and revise policies to reflect the latest legal requirements for 2026.
Conclusion: Build Resilience Before the Next Attack
One-time projects do not win battles in cybersecurity; it is a continuous process entailing assessment, improvement, and staying vigilant. Digital threats in 2026 will be faster, smarter, and more adaptive, enabled by AI and automation. But with the right protocols in place, your business can remain one step ahead.
By adopting Zero Trust, enforcing MFA, encrypting data, securing the cloud, training employees, and investing in proactive monitoring, you create not just a secure business-but a resilient one.
That is the clear message: don’t wait until it happens. Begin strengthening your cybersecurity foundation today and make 2026 the year your business becomes truly cyber resilient.

A Developer’s Guide to Building Cross-Platform Apps: Flutter vs React Native vs Kotlin Multiplatform
Introduction:
One Codebase, Many Platforms
Take an application written in one code and execute it perfectly on Android, iOS, the web, and even desktops without compromising performance or user experience. That is what cross-platform app development is promising, and it has become a trend that has changed the way developers look at mobile and software engineering.
And the days when the two codebases had to be maintained, and two times the effort was necessary to make each update of the codebase. In 2026, systems such as Flutter, React Native, and Kotlin Multiplatform are leading this market, providing unusual methods of simplifying the creation of apps without making them slower than usual.
But which one of you are you choosing? We are going to unearth the technical richness, strengths, and weaknesses of these frameworks and identify which one may be the most suitable for your future big idea.
Understanding the Cross-Platform Concept:
The development of cross-platforms is concerned with efficiency and accessibility. Rather than developing code on a per-platform basis, the developers make a common codebase to run across the operating systems.
The advantages are unquestionable: quicker time to market, cheaper, and maintenance. It is, however, a challenge to make these apps appear and work like actual native experiences. At that point, there are modern frameworks that combine common logic with platform-based optimizations.
We will consider how Flutter, React Native, and Kotlin Multiplatform would solve this issue in different ways.
Flutter: The Power of Widgets and Design Freedom
Google created Flutter, a full set of UI that enables developers to create high-performance applications across several platforms in the Dart programming language.
The most notable characteristic is its architecture in the form of a widget. Flutter text, buttons, layouts, and animations are all widgets, and the widgets are rendered directly to the screen through the Skia rendering engine. This implies that your app interface is not built on native components, which brings your app the absolute freedom to decide what your app should and can look like.
The fact that Flutter is compiled to native ARM code makes it very impressive, as there is no longer the need to bridge between the app logic and the native components. It is a favorite among developers because of a feature known as hot reload, which allows one to quickly preview changes without making them restart the whole app.
Pros of Flutter:
- Unified UI: It is possible to create pixel-perfect interfaces that appear exactly the same on iOS and Android.
- Rapid performance: Bridgeless compilation to native code.
- Good community: Google supported with huge documentation and plugins.
- Single platform code: Best when time is of the essence and when the team is small.
Cons of Flutter:
- Huge app size: Flutter binaries are heavier because they have embedded engines.
- Dart learning curve: Developers should learn Dart, which is not as familiar as JavaScript.
- Non-native appearance: The apps do not necessarily fit the aesthetic of the platform since they are not based on native UI elements.
React Native: Familiarity Meets Flexibility
Another ecosystem heavyweight is React Native, which is developed by Meta (Facebook). It enables developers to create mobile applications in JavaScript and React and connects the world of web and mobile development.
React Native, unlike Flutter, does not use native UI components; therefore, your app looks and feels like a native one. It has an underlying bridge between JavaScript logic and native APIs. This bridge may introduce a certain amount of latency, but the new Fabric architecture and JSI (JavaScript Interface) of the framework have increased speed and responsiveness many times over.
React Native is also one of the simplest frameworks to learn because developers already familiar with React can simply switch to it when developing a web application.
Pros of React Native:
- Pulls on web development knowledge: Salesforce acquires JavaScript and React knowledge more quickly.
- Native performance and feel: Native components are used, providing a more native user experience.
- Liquid ecosystem: Thousands of open-source libraries and tools to choose from.
- Hot Reload: Does not require extensive testing and development cycles.
Cons of React Native:
- Bridge performance problems: Sometimes, the interaction between JavaScript and native code may introduce a delay in complicated applications.
- Dependency management by a third party: there are some plugins that are not automatically updated with OS changes, or that incompatibility.
- Ineffective inconsistency UI: iOS and Android versions have inconsistent visual differences, which might need to be changed manually.
Kotlin Multiplatform: The Native-First Hybrid
Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP), JetBrains, provides a radically different solution. It does not require developers to create a one-size-fits-all UI; instead, developers can reuse core business logic (such as networking, database, and domain layers) and remain native with the UI.
This has seen KMP become popular among enterprise developers who desire performance and still have platform authenticity. It is fully compatible with any existing Android projects, meaning that developers can step-by-step integrate the logic between iOS, desktop, or web apps.
KMP is constructed with Kotlin, a modern, type-safe language that Google supports to its full extent to develop Android applications, and it translates to native code with Kotlin/Native.
Pros of Kotlin Multiplatform:
- Native performance: Shared code targets the native binaries of a platform.
- Flexibility: Select the degree of cross-platform sharing.
- Native UI: Jetpack Compose (Android) and SwiftUI (iOS) will be used as platform-specific interfaces.
- Gradual adoption: Ideal in the case of current native teams that want to go cross-platform.
Cons of Kotlin Multiplatform:
- Reduced reuse of UI: UIs will have to be developed on an individual platform basis.
- Small community and fewer prepared libraries: Ecosystem at its early stage.
- Complex configuration: This requires one to be acquainted with both Android and iOS.
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Flutter | React Native | Kotlin Multiplatform |
| Language | Dart | JavaScript / TypeScript | Kotlin |
| UI Framework | Custom Widgets (Skia) | Native Components | Native (Compose / SwiftUI) |
| Performance | Excellent (native-compiled) | Good (bridge overhead) | Excellent (native binaries) |
| Code Sharing | Up to 100% | ~80% | Logic Layer Only |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Easy | Moderate |
| Community Size | Large, growing | Largest | Smaller but expanding |
| Best Use Case | Visually rich multi-platform apps | Apps requiring native look & quick dev | Enterprise, high-performance apps |
| Backed By | Meta (Facebook) | JetBrains / Google |
Choosing the Right Framework:
The optimal structure relies on your objectives, resources as well as long-term strategy.
Flutter will be the leader of choice in case you enjoy gorgeous, cohesive UIs and rapid rendering. The design is similar on all the devices as well as the simplicity of testing; it best suits startups and design-oriented applications.
React Native should be used by teams already familiar with JavaScript, who are only interested in MVPs, startups, and projects that need rapid iteration, because it provides familiar syntax and wide community support.
In the meantime, Kotlin Multiplatform provides the most desirable of the two worlds, the native performance with the shared logic. It is especially applicable to organizations that already utilize Kotlin, or those that wish to modernize the applications that are already available on Android without having to recompile them.
Conclusions: Cross-Platform Development in the Future
By the year 2026, the development of cross-platforms will be more necessary than convenient. A question that is no longer debatable is whether these frameworks can produce quality apps. The question now is which of them fits your philosophy of development best.
Flutter is at the forefront of unified, cross-platform, high-performance experiences. React Native remains the best as it has an enormous ecosystem and supports JavaScript. In the meantime, Kotlin Multiplatform is gradually becoming the enterprise favorite, with its ability to provide organizations with unparalleled flexibility in the process of sharing logic without sacrificing the native advantage.
Regardless of the framework that you adopt, your app will eventually succeed or fail depending on a well-considered architecture, an excellent UX design, and constant optimization. The instruments are more potent than ever before, and now it is up to the developers to be creative with them.
Whether you are making the next social media sensation, a financial tech dashboard, or a cross-gadgets productivity platform, the framework you select now will determine your digital presence over the next few years.
